Участник:Burrito Justice/Sandbox
Atmospherics: The Department
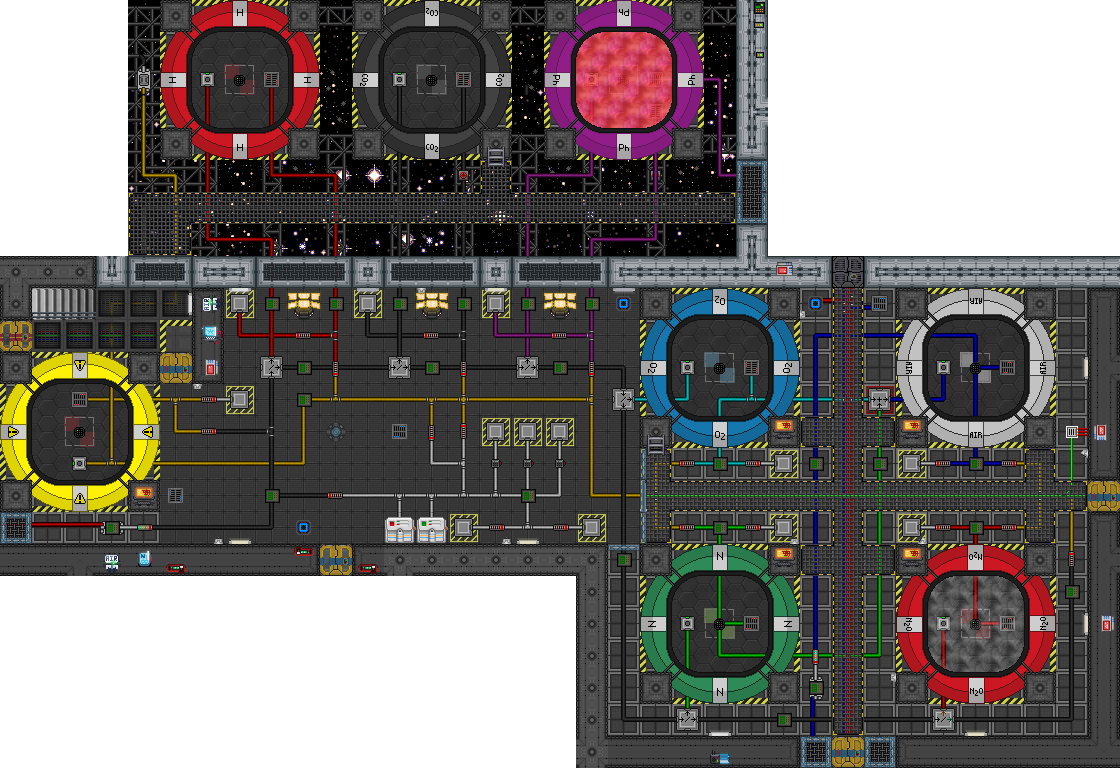
Welcome to Atmospherics, the place where Dreams Come True™. Or at least the place that can partially sustain the ability to dream... y'know, by allowing you to breathe and stuff. Breathing is important, and the primary function of this maze of pipes and gas is to distribute breathable air throughout the station efficiently, and to restore air to depressurized - but hopefully air-tight - rooms. Its secondary function is to process contaminant gases captured by the scrubber network and sort the gas accordingly into one of many chambers.
If you're new to all of this - or even just someone who's never really given Atmos a fair shake - then this will all look very complex and downright intimidating to look at. This mostly stems from just how much stuff can get on screen at once, but there's a few things put in place to make pipe-readability easier on the user if they just take the time to truly examine what each pipe network is meant to do. Alongside that will be this guide to help you out.
What Do These Colors Mean?
So there's a lot of pipes with a bunch of colors and they all look really important. It's true that all of the colored pipes - which represent different pipe networks - have their place in the department, but not all of them are strictly necessary to produce gas. Here's all of the important colors, though note that the colored pipes beneath the catwalks aren't to be taken into account:
- Air Mix: This is the air mix loop, and these pipes are the most important: they're the ones that contain the air mix, which is combined at a mixer set to specific percentages to ensure that the gas everyone breathes is, in fact, breathable. Tampering with the mixer is ill-advised, as is modifying this network in such a way that it will not be able to reach the distribution network.
- Distribution: Equally important is this blue network, offset pipes to the south alongside the scrubber pipes. This massive network of pipes is what will actually distribute the air that it receives from the air mix loop and send it all towards vents placed all around the station, ensuring every room remains at optimal pressure.
- Filtering: These pipes are part of the filtering network, a pipe line connected to the scrubber network that leads to filtering devices which will filter a select gas out of the line and output it into a large storage chamber full of that same gas. If the gas type does not match then it'll continue down the line until it eventually does reach where it's meant to go. If, somehow, it reaches the end of the line and doesn't match any of the filtering criteria then it will just be output into the mix loop.
- Scrubber: You'll probably notice some pipe adapters and pipes that aren't centered towards the south of Atmos proper. These pipes are part of the scrubber network and, as you can imagine, much of this network is comprised of scrubbers. The end of this line - where all of the scrubber pipe contents are pumped out towards - is the filtering line.
- Mix: This line is a bit odd, but its intended function is to provide a pipe network that you can pump any of the gases in atmos into, allowing you to make custom mixes and letting you warm them up or cool them down. Using this line isn't necessary for Atmos to function, but it's good to use as a test bed of sorts if you'd like to experiment with how devices interact with pipe networks. Note that part of this network is colorless.
- Misc Mix: These pipes aren't actually part of a network, they just pipe oxygen and nitrogen into a mixer which outputs into the air chamber which later outputs into the air mix line.
- Waste: These are the black pipes, as few as they are, towards the southern end of Atmos proper. It's intended function is to eject undesirable gas out into space harmlessly, usually by pumping gas you don't want filtered into it from either the mix line or the filter line by way of pumps, and turning a valve open to space.
Principles and Concepts
Pressure
Delta P
watch out for that pressure differential. also 200 kpa ambient pressure blah blah
Temperature
e x p a n d
Specific Heat
factors into heat capacity
Volume
Mass
moles moles moles
Math
See this section for volume of pipes
Pressure (in kPa) * Volume = Moles * 8.314 (the molar gas constant) * temperature (in Kelvin. Kelvin = Celsius + 273.15)
Gas Gas Gas
 Oxygen (O2): 20 SH, 0.032 MM, oxidizer, necessary for life
Oxygen (O2): 20 SH, 0.032 MM, oxidizer, necessary for life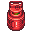 Nitrogen (N2): 20 SH, 0.028 MM, inert, non-toxic
Nitrogen (N2): 20 SH, 0.028 MM, inert, non-toxic Air (Air): 79% N2 21% O2, if you wanna sound like a nerd then call it nitrox
Air (Air): 79% N2 21% O2, if you wanna sound like a nerd then call it nitrox Carbon Dioxide (CO2): 30 SH 0.044 MM, toxic in concentrations greater than or equal to 7 kPa
Carbon Dioxide (CO2): 30 SH 0.044 MM, toxic in concentrations greater than or equal to 7 kPa Nitrous Oxide (N2O): No, it's not N20, it's N2O. Jamming twenty nitrogen molecules together would be stupid. 40 SH 0.044 MM, sleep agent, oxidizer
Nitrous Oxide (N2O): No, it's not N20, it's N2O. Jamming twenty nitrogen molecules together would be stupid. 40 SH 0.044 MM, sleep agent, oxidizer Hydrogen (H2): 100 SH 0.002 MM, fuel, non-toxic
Hydrogen (H2): 100 SH 0.002 MM, fuel, non-toxic Phoron (PH): 200 SH 0.405 MM, fuel, toxic, contaminant
Phoron (PH): 200 SH 0.405 MM, fuel, toxic, contaminant
Relevant Tools
necessary stuff you'll maybe want
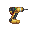 Impact Wrench: The impact wrench (or power drill, if you prefer) is a tool that condenses a screwdriver and wrench down into one tool. As you've probably found out by now, activating the item in hand will change its bit. For pipes you'll want a wrench bit in order to either secure or unsecure pipe sections and other devices. It cannot unwrench a pipe if its internal pressure exceeds 200 kPa over ambient pressure.
Impact Wrench: The impact wrench (or power drill, if you prefer) is a tool that condenses a screwdriver and wrench down into one tool. As you've probably found out by now, activating the item in hand will change its bit. For pipes you'll want a wrench bit in order to either secure or unsecure pipe sections and other devices. It cannot unwrench a pipe if its internal pressure exceeds 200 kPa over ambient pressure. Wrench: If you're missing an impact wrench then you probably have this instead. When it comes to pipe interaction there is no difference between this tool and its powered counterpart.
Wrench: If you're missing an impact wrench then you probably have this instead. When it comes to pipe interaction there is no difference between this tool and its powered counterpart. Pipe Wrench: As the name might imply this tool is specialized towards dealing with pipes. The pipe wrench's biggest advantage over other wrenches is that it can unsecure a pipe at any pressure. It's also able to
Pipe Wrench: As the name might imply this tool is specialized towards dealing with pipes. The pipe wrench's biggest advantage over other wrenches is that it can unsecure a pipe at any pressure. It's also able to manglebend or straighten simple pipe segments if they are not already secured. This comes at the price of being unable to function like a normal wrench for anything other than pipes and atmospheric devices. Gas Analyzer: This tool is invaluable to any aspiring atmos tech. Though some may argue you should already have an innate sense of exactly what's inside a pipe via telepathy (you're the person in charge of that gas, you put it in that pipe!!!) this shouldn't stop you from deciding to use a tool like the analyzer. Once upon a time this device did pretty much nothing but now it can be used to measure the following:
Gas Analyzer: This tool is invaluable to any aspiring atmos tech. Though some may argue you should already have an innate sense of exactly what's inside a pipe via telepathy (you're the person in charge of that gas, you put it in that pipe!!!) this shouldn't stop you from deciding to use a tool like the analyzer. Once upon a time this device did pretty much nothing but now it can be used to measure the following:
It can also be used to analyze gas on the turf you're standing in by activating it in hand.
 Pipe Dispenser: Despite the fact that this object cannot be held, it is still a tool. Put simply, when secured to the floor (with a wrench) in a powered area, this device will vend pretty much anything under the pipes subheading, giving you plenty of options. Oddly enough securing this to the floor is faster than unsecuring it. The more you know.
Pipe Dispenser: Despite the fact that this object cannot be held, it is still a tool. Put simply, when secured to the floor (with a wrench) in a powered area, this device will vend pretty much anything under the pipes subheading, giving you plenty of options. Oddly enough securing this to the floor is faster than unsecuring it. The more you know. Rapid Fabrication Device - Pipes: The handheld version of the pipe dispenser, the RFD-P is capable of... well, pretty much everything its bigger cousin can do, though with a smaller list of pipes and devices that can be created, heat exchange pipes most notably having gone missing. Activating the item in hand will bring up a list of pipes, and alt-clicking it will swap through device categories. The RPD requires matter cartridges in order to operate, but thankfully the ones that can be found in lockers are already loaded.
Rapid Fabrication Device - Pipes: The handheld version of the pipe dispenser, the RFD-P is capable of... well, pretty much everything its bigger cousin can do, though with a smaller list of pipes and devices that can be created, heat exchange pipes most notably having gone missing. Activating the item in hand will bring up a list of pipes, and alt-clicking it will swap through device categories. The RPD requires matter cartridges in order to operate, but thankfully the ones that can be found in lockers are already loaded.- Файл:Multitool.pngMultitool: Perhaps an unexpected addition, but the multitool actually does have a use in the land of pipes, as niche as it is. It is used to flip which overlapping pipe network a meter observes. For instance, if one network crosses from east to west and another network crosses from south to north on the same turf, and a multitool is secured over these pipes, using a multitool on it will swap between both pipe nets. Figuring out which is which is as simple as waving your gas analyzer over a network and comparing the readings.
Pipes and Devices
Stuff can be rotated with alt click lol
Basic Pipes
Many of these pipes have distro and scrubber variants.
 Straight: The most common type of pipe you will see. It goes straight from one direction to another. It holds up to 70L.
Straight: The most common type of pipe you will see. It goes straight from one direction to another. It holds up to 70L.
 Manifold: A pipe with three ends on it instead of two. Holds up to 105L.
Manifold: A pipe with three ends on it instead of two. Holds up to 105L. Four Way: Even better than the previous entry, this one has four ends. Whooooaaaa. Holds up to 140L.
Four Way: Even better than the previous entry, this one has four ends. Whooooaaaa. Holds up to 140L.- Файл:Pipecap.pngCap: A bit that simply closes off the end of a pipe with a cap. There's no real reason to use this, especially since pipes don't leak, but it holds up to 35L regardless.
- Файл:Zpipe.pngZ-Pipe: A pipe piece that connects one level to another. Holds 70L, but since you need at least two to make this work it's effectively 140L.
 Universal Pipe Adapter: This special piece of work will connect different pipe types together, namely normal, distro, and scrubber pipes. This can make for some rather creative pipe setups if you don't mind a few pipes being colored red or blue. Holds up to 70L.
Universal Pipe Adapter: This special piece of work will connect different pipe types together, namely normal, distro, and scrubber pipes. This can make for some rather creative pipe setups if you don't mind a few pipes being colored red or blue. Holds up to 70L.- Файл:PipeHE.pngHeat Exchange: Special pipe designed in a way to equalize heat with the gas inside and the environment that it's in. In other words, if you pipe super cooled gas into heat exchange pipes winding around a room that's normally at room temperature, then the room will cool down and the gas will heat up. Holds up to 70L.
- Файл:PipeHEJ.pngJunction: Weirdly enough, pipe adapters cannot connect heat exchangers to normal pipes, requiring the use of this special pipe. On one end goes normal pipes and on the other goes heat exchange pipes. You can figure it out.
- Файл:Pipeinsulated.pngInsulated: Extremely niche pipes, these have no special use other than reinforcing pipes well beyond what's necessary. Only consists of straight pipes, meaning there's no manifolds or four-ways. Holds up to 70L.
Devices and Utilities
most powered devices use 150 watts when idle, most devices capable of pumping gas will consume one watt to one kPa.
Non-Pipe
 Pipe Meter: A device that will observe whatever pipe network it is secured onto. It will tell you the temperature and pressure of the network, even from a distance, and it even gives visual indicators of the pressure! This won't replace gas analyzers, though, since it can neither determine how many moles are in a net nor can it determine what gases are in the network. You can use a multitool to switch which network a meter pays attention to assuming it's secured over overlapping pipes.
Pipe Meter: A device that will observe whatever pipe network it is secured onto. It will tell you the temperature and pressure of the network, even from a distance, and it even gives visual indicators of the pressure! This won't replace gas analyzers, though, since it can neither determine how many moles are in a net nor can it determine what gases are in the network. You can use a multitool to switch which network a meter pays attention to assuming it's secured over overlapping pipes. Turf Meter: The pipe meter's slightly awkward cousin, this will measure the gas on the turf that it is secured upon. It's functionally similar to the pipe meter otherwise.
Turf Meter: The pipe meter's slightly awkward cousin, this will measure the gas on the turf that it is secured upon. It's functionally similar to the pipe meter otherwise. Gas Sensor: What could be considered an advanced turf meter, minus the visual indicators. In fact, this device requires a specific console in order to see what it's reading. It can determine pressure, temperature, and gas concentrations. You'll probably see these in the large gas chambers.
Gas Sensor: What could be considered an advanced turf meter, minus the visual indicators. In fact, this device requires a specific console in order to see what it's reading. It can determine pressure, temperature, and gas concentrations. You'll probably see these in the large gas chambers.
Unary
 Connector: Definitely one of the most important utilities in any atmos setup, this will allow you to connect any portable atmospheric device to to a pipe network with a wrench, typically canisters. Anything connected to one of these will automatically balance the gases between the connected device and the connected pipe network.
Connector: Definitely one of the most important utilities in any atmos setup, this will allow you to connect any portable atmospheric device to to a pipe network with a wrench, typically canisters. Anything connected to one of these will automatically balance the gases between the connected device and the connected pipe network. Heat Exchanger: Not to be confused with the heat exchange pipes seen above, this radiator is designed to face another heat exchanger in order to balance heat between two networks without actually mixing the gases together.
Heat Exchanger: Not to be confused with the heat exchange pipes seen above, this radiator is designed to face another heat exchanger in order to balance heat between two networks without actually mixing the gases together. Tank: A massive, immobile tank of gas that has a capacity of 10000L. They can neither be built nor deconstructed. They're only found in the command bunker, emergency atmos substation near the docks, and in telecomms. Not to be confused with canisters or small handheld tanks.
Tank: A massive, immobile tank of gas that has a capacity of 10000L. They can neither be built nor deconstructed. They're only found in the command bunker, emergency atmos substation near the docks, and in telecomms. Not to be confused with canisters or small handheld tanks. Gas Cooler: A large device that is capable of cooling the contents of a pipe network to near-Absolute Zero values. How fast it cools and how large its volume is depends on upgrades made to it. Holds 600L by default.
Gas Cooler: A large device that is capable of cooling the contents of a pipe network to near-Absolute Zero values. How fast it cools and how large its volume is depends on upgrades made to it. Holds 600L by default. Gas Heater: A large device that is capable of heating the contents of a pipe network to rather high values. How fast it heats and how large its volume is depends on upgrades made to it. Holds 600L by default.
Gas Heater: A large device that is capable of heating the contents of a pipe network to rather high values. How fast it heats and how large its volume is depends on upgrades made to it. Holds 600L by default. Air Injector: A device whose whole purpose is to pump gas (not just air, like the name implies) onto a turf, similar to a vent pump, except it's rated to pressurize up to 15000 kPa. Usually controlled from a special console. Holds 700L, allows a flow rate of up to 700L/s, rated to pressurize up to 15000 kPa, can consume up to 15 kW at max operational capacity.
Air Injector: A device whose whole purpose is to pump gas (not just air, like the name implies) onto a turf, similar to a vent pump, except it's rated to pressurize up to 15000 kPa. Usually controlled from a special console. Holds 700L, allows a flow rate of up to 700L/s, rated to pressurize up to 15000 kPa, can consume up to 15 kW at max operational capacity. Vent Pump (Unary Vent): The device that you'll probably see the most around the station, these vents are typically controlled by an air alarm to determine what pressure to target. Special versions of this vent allow it to siphon gas indiscriminately instead, a notable example being the vent pump in the SM core. Vents performing both functions can be found in airlocks. Holds up to 200L, allows a flow rate of up to 200L/s, rated to pressurize to 7500 kPa, can consume up to 7.5 kW at max operational capacity.
Vent Pump (Unary Vent): The device that you'll probably see the most around the station, these vents are typically controlled by an air alarm to determine what pressure to target. Special versions of this vent allow it to siphon gas indiscriminately instead, a notable example being the vent pump in the SM core. Vents performing both functions can be found in airlocks. Holds up to 200L, allows a flow rate of up to 200L/s, rated to pressurize to 7500 kPa, can consume up to 7.5 kW at max operational capacity. Scrubber: Where a vent pump (usually) pumps a gas (typically air) into a room, scrubbers do the opposite, with a twist: they can be controlled by an air alarm to target and collect any type of gas and pump it into a pipe network while leaving other gases alone. It can also be set to forcefully siphon gas indiscriminately, giving it a lot more power. Holds up to 200L, allows a flow rate of up to up to 200L/s, 2500L/s on siphon, rated to pressurize to 7500 kPa, can consume 7.5 kW at max operational capacity.
Scrubber: Where a vent pump (usually) pumps a gas (typically air) into a room, scrubbers do the opposite, with a twist: they can be controlled by an air alarm to target and collect any type of gas and pump it into a pipe network while leaving other gases alone. It can also be set to forcefully siphon gas indiscriminately, giving it a lot more power. Holds up to 200L, allows a flow rate of up to up to 200L/s, 2500L/s on siphon, rated to pressurize to 7500 kPa, can consume 7.5 kW at max operational capacity. Cryo Cell: Maybe not immediately concerning to your average pipe enthusiast, the cryo cell is nonetheless an atmospheric utility. It's connected to a pipe network that hopefully has chilled oxygen, which can be used to put a patient in stasis and heal some of their wounds. See the guide to medicine for more info.
Cryo Cell: Maybe not immediately concerning to your average pipe enthusiast, the cryo cell is nonetheless an atmospheric utility. It's connected to a pipe network that hopefully has chilled oxygen, which can be used to put a patient in stasis and heal some of their wounds. See the guide to medicine for more info.
Binary
 Pressure Regulator: An often overlooked device, this programmable gate allows for a number of tasks. It can be programmed to allow gas through until the output end is greater than or equal to the target pressure, or it can be programmed to allow gas through when its input end reaches the target pressure, and will stay open until the input end is less than or equal to the target pressure. All of this comes at the cost of being unable to pump gas; if its input is at a lower pressure than the output, gas cannot flow through. In order to allow the regulator to do its job the valve must be unlocked. The end with the bright red valve is the output end. Both ends of the regulator hold 500L, making this effectively 1000L, allows a flow rate of up to 500L/s.
Pressure Regulator: An often overlooked device, this programmable gate allows for a number of tasks. It can be programmed to allow gas through until the output end is greater than or equal to the target pressure, or it can be programmed to allow gas through when its input end reaches the target pressure, and will stay open until the input end is less than or equal to the target pressure. All of this comes at the cost of being unable to pump gas; if its input is at a lower pressure than the output, gas cannot flow through. In order to allow the regulator to do its job the valve must be unlocked. The end with the bright red valve is the output end. Both ends of the regulator hold 500L, making this effectively 1000L, allows a flow rate of up to 500L/s.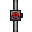 Manual Valve: A simple gate that allows you to connect two networks together or shut them off from each other. Note that neither the AI nor its borgs can operate these valves. It also contains no volume, oddly enough.
Manual Valve: A simple gate that allows you to connect two networks together or shut them off from each other. Note that neither the AI nor its borgs can operate these valves. It also contains no volume, oddly enough.
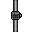 Digital Valve: Exactly the same as the manual valve, except it cannot be unsecured, for reasons beyond comprehension. It also cannot be vended from a pipe dispenser. If you carefully observe where these valves are located you might be able to determine what their true purpose is. They can also be operated by the AI and its borgs.
Digital Valve: Exactly the same as the manual valve, except it cannot be unsecured, for reasons beyond comprehension. It also cannot be vended from a pipe dispenser. If you carefully observe where these valves are located you might be able to determine what their true purpose is. They can also be operated by the AI and its borgs.
- Файл:Circulator.pngTEG Circulator: This is just one part of a thermoelectric generator. Basically it takes gas in on one end and outputs it on another end. Which end is what can be determined by examining the circulator. Each end holds 200L, making this effectively 400L, allows a flow rate of up to 200L/s (probably).
 Gas Pump: A strong staple in any pipe setup, this will attempt to force gas on its input end into the output end for as long as the gas on the output end is at a lower pressure than target, and there is gas in the input end. The pump is smart and will just let gas through if the output end is at a lower pressure than the input end, but the pump's effectiveness will decrease dramatically if the pressure on the input end is well below the pressure of the output pipe. The output end is the bit with the red stripe on it. Each end holds 200L, making this effectively 400L, allows a flow rate of up to 200L/s, rated to pressurize to 7500 kPa, can consume up to 7.5 kW at max operational capacity.
Gas Pump: A strong staple in any pipe setup, this will attempt to force gas on its input end into the output end for as long as the gas on the output end is at a lower pressure than target, and there is gas in the input end. The pump is smart and will just let gas through if the output end is at a lower pressure than the input end, but the pump's effectiveness will decrease dramatically if the pressure on the input end is well below the pressure of the output pipe. The output end is the bit with the red stripe on it. Each end holds 200L, making this effectively 400L, allows a flow rate of up to 200L/s, rated to pressurize to 7500 kPa, can consume up to 7.5 kW at max operational capacity.
 High Power Pump: The big sister of the gas pump, the high power pump can target higher pressures. The output end is the bit with the red stripe on it. Each end holds 200L, making this effectively 400L, allows a flow rate of up to 200L/s, rated to pressurize to 15000 kPa, can consume 15 kW at max operational capacity.
High Power Pump: The big sister of the gas pump, the high power pump can target higher pressures. The output end is the bit with the red stripe on it. Each end holds 200L, making this effectively 400L, allows a flow rate of up to 200L/s, rated to pressurize to 15000 kPa, can consume 15 kW at max operational capacity.
Ternary/Quaternary
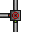 T-Valve: A bit of an odd specimen, this valve has one input and two potential outputs, but at least one of them will always be closed, and neither of them can be open or closed at the same time. The indicator lights will tell you which side is open and which is closed, and turning the valve will toggle which output is opened. The AI and its borgs cannot operate the valve. There is also a mirrored variant.
T-Valve: A bit of an odd specimen, this valve has one input and two potential outputs, but at least one of them will always be closed, and neither of them can be open or closed at the same time. The indicator lights will tell you which side is open and which is closed, and turning the valve will toggle which output is opened. The AI and its borgs cannot operate the valve. There is also a mirrored variant.
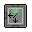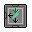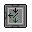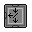 (Omni) Gas Filter: The gas filter is an impressive device that is capable of pumping gas through to another network while scrubbing a target gas out into a different, perpendicular network. A series of these set to different gases is what allows the filtering line of Atmospherics to function. There is a mirrored variant of this device as well. There is also a much more flexible omni variant, which allows you to set which side is the input, output, and allows you to set two more sides as filters. Each programed side holds 200L, making this effectively 800L assuming an omni filter is set to have all four sides in use, allows a flow rate of up to 200L/s, rated to pressurize up to 7500 kPa, can consume up to 7.5 kW at max operational capacity.
(Omni) Gas Filter: The gas filter is an impressive device that is capable of pumping gas through to another network while scrubbing a target gas out into a different, perpendicular network. A series of these set to different gases is what allows the filtering line of Atmospherics to function. There is a mirrored variant of this device as well. There is also a much more flexible omni variant, which allows you to set which side is the input, output, and allows you to set two more sides as filters. Each programed side holds 200L, making this effectively 800L assuming an omni filter is set to have all four sides in use, allows a flow rate of up to 200L/s, rated to pressurize up to 7500 kPa, can consume up to 7.5 kW at max operational capacity. (Omni) Gas Mixer: As the name implies, this device mixes gas together, usually by taking two input gases (which can already have been mixed up by something else) and outputting the combined result into a pipe with programmed concentrations. One of these devices is what allows the air line of Atmospherics to maintain a strict 79% N2 21% O2 air mix. There is a mirrored variant of this device as well. There is also a much more flexible omni variant, which allows you to set which direction the inputs are and where the output goes. Each programmed side holds 200L, making this effectively 800L assuming an omni filter is set to have all four sides in use, allows a flow rate of up to 200L/s, rated to pressurize up to 7500 kPa, can consume up to 7.5 kW at max operational capacity.
(Omni) Gas Mixer: As the name implies, this device mixes gas together, usually by taking two input gases (which can already have been mixed up by something else) and outputting the combined result into a pipe with programmed concentrations. One of these devices is what allows the air line of Atmospherics to maintain a strict 79% N2 21% O2 air mix. There is a mirrored variant of this device as well. There is also a much more flexible omni variant, which allows you to set which direction the inputs are and where the output goes. Each programmed side holds 200L, making this effectively 800L assuming an omni filter is set to have all four sides in use, allows a flow rate of up to 200L/s, rated to pressurize up to 7500 kPa, can consume up to 7.5 kW at max operational capacity.
Portables
blah blah blah
 Canisters: Probably the most common form of portable atmospherics, a canister can hold up to 1000L of gas, and (miraculously) can withstand an infinite amount of pressure and temperature. This doesn't mean they're indestructible - they can rupture due to explosions nearby... or just because a random event told it to rupture. They have their own internal pressure regulator rated up to 1013 kPa, and can either be allowed to pressurize its turf and surroundings up to that pressure (assuming it has enough gas) or it can be used to fill handheld tanks up to that pressure. Not to be confused with handheld tanks or the much larger tank which sort of accomplishes the same goal.
Canisters: Probably the most common form of portable atmospherics, a canister can hold up to 1000L of gas, and (miraculously) can withstand an infinite amount of pressure and temperature. This doesn't mean they're indestructible - they can rupture due to explosions nearby... or just because a random event told it to rupture. They have their own internal pressure regulator rated up to 1013 kPa, and can either be allowed to pressurize its turf and surroundings up to that pressure (assuming it has enough gas) or it can be used to fill handheld tanks up to that pressure. Not to be confused with handheld tanks or the much larger tank which sort of accomplishes the same goal. Portable Air Pump: Basically a fancier canister, but with a pump, rated to pressurize up to 1013 kPa, at a rate of a whopping 1000L/s! This is capable of pumping gas out into surrounding turfs or pumping gas into itself from surrounding turfs. Pumps, of course, require power, hence this device possessing a power cell. The cell can be retrieved by screwing it out. The pump can both fill or empty a tank inserted into it. Can hold up to 1000L.
Portable Air Pump: Basically a fancier canister, but with a pump, rated to pressurize up to 1013 kPa, at a rate of a whopping 1000L/s! This is capable of pumping gas out into surrounding turfs or pumping gas into itself from surrounding turfs. Pumps, of course, require power, hence this device possessing a power cell. The cell can be retrieved by screwing it out. The pump can both fill or empty a tank inserted into it. Can hold up to 1000L. Portable Scrubber: This particular curio is basically a non-programmable scrubber that will scrub anything that isn't nitrogen or oxygen from the air. Its pump is rated to pressurize up to 1013 kPa at a rate of 200L/s. It will not use power if it is turned on and there are no gases to scrub. It will scrub contaminants (anything that isn't oxygen or nitrogen) from any connected tank while turned on. Like the portable air pump, this too requires power, and has a power cell that can be replaced by screwing it out. Holds up to 750L, allows a flow rate of up to 200L/s.
Portable Scrubber: This particular curio is basically a non-programmable scrubber that will scrub anything that isn't nitrogen or oxygen from the air. Its pump is rated to pressurize up to 1013 kPa at a rate of 200L/s. It will not use power if it is turned on and there are no gases to scrub. It will scrub contaminants (anything that isn't oxygen or nitrogen) from any connected tank while turned on. Like the portable air pump, this too requires power, and has a power cell that can be replaced by screwing it out. Holds up to 750L, allows a flow rate of up to 200L/s. Hydroponics Tray: Bet you weren't expecting to see this here. It's true, plant trays do have gas interactions which can be controlled by hooking it into a connector and flipping the lid down. The plants (assuming they're mutated and not dead) will passively generate gas, and are capable of outputting this into pipes if the tray is connected to a pipe network. The tray is capable of holding up to 100L.
Hydroponics Tray: Bet you weren't expecting to see this here. It's true, plant trays do have gas interactions which can be controlled by hooking it into a connector and flipping the lid down. The plants (assuming they're mutated and not dead) will passively generate gas, and are capable of outputting this into pipes if the tray is connected to a pipe network. The tray is capable of holding up to 100L.
Handhelds
tanks bruh
Unimplemented
- Passive Vent: Effectively just a pipe that's allowed exchanging gas contents with the turf it's secured upon. As you can imagine, a passive vent connected to an empty pipe exposed to a turf of air will fill the pipe with air. While it does have its uses, it's not seen in the pipe dispenser list for some reason.
- Binary Vent Pump: Basically a vent pump, except it has two ends where you can connect pipes. One end is the input - for when it's pumping gas into a room -, and the other end is the output - for when the vent siphons gas instead. Not seen anywhere on the Aurora and otherwise unobtainable.
- Oxygen Generator: An absolute dinosaur, this device hasn't been used since ye olden days. As the name implies it produces pure oxygen... from nothing. Normally connected to a pipe on one end. There's a pretty good chance that this doesn't work anymore.
- Thermal Plate: One may believe that this was a precursor to the heat exchange pipe, but this was actually created after. Anyway this was connected to a pipe on one end and would exchange heat with the turf it was secured on. You would need dozens of these with some awkward pipe work to accomplish what simple spaghetti HE pipes can accomplish now.
- Thruster: Probably related to overmap functions. Assuming that's the case, this would just eject gas to produce thrust for overmap shuttles.
- Pipe Turbine: This was effectively a condensed version of the gas turbine. It would produce energy by piping extremely high pressure gas (usually superheated) to turn a turbine, assuming it was connected directly to a special generator. Even when this was developed way back when, it was never really used that much, and it's not seen anywhere on the Aurora. It probably doesn't work anymore, even if you manage to find a setup.
Breathe That Air
something about how stuff works in practice? idk
Air Alarm Operation
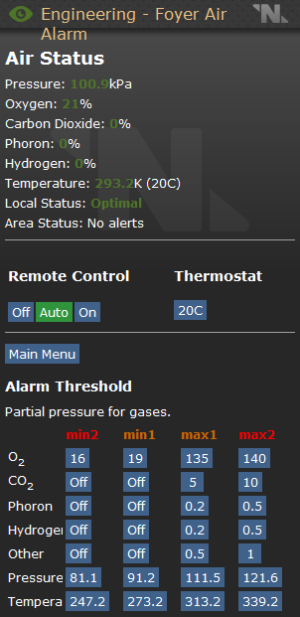
how to work that dumb air alarm
PHORON CHECK!
*face melts off*